Cloudflare Cron Trigger using Resend
Small introduction on how to use a cron trigger using Cloudflare Workers. For this example I will create a cron trigger that every 3 hours sends an email and “processes” data from a Cloudflare KV.
To start we need an api key the Resend that we will add to a .dev.vars file and a verified domain, as we are testing we can use onboarding@resend.dev. We also need a binding for our KV and for our cron trigger.
We add these things and create some functions to add an element and to read an element from our KV.
This will tell Workers when to run the cron (every 3 hours in this case) and which KV to point to:
// wrangler.jsonc
"triggers": {
"crons": ["0 */3 * * *"],
},
"kv_namespaces": [
{
"id": "a5417ae738294c36b56f3e132138e9fdca",
"binding": "KV_BINDING",
},
],
// worker-configuration.d.ts
interface Env {
KV_BINDING: KVNamespace;
RESEND_API_KEY: string;
}
// kv.ts
export async function postKv(request: Request, env: Env): Promise<Response> {
const data = (await request.json()) as Record<string, unknown>;
const createKey = `task:${Date.now()}:${crypto.randomUUID()}`;
await env.KV_BINDING.put(
createKey,
JSON.stringify({
...(data as object),
Date: Date.now(),
status: 'pending',
}),
);
return new Response('Task Added');
}
export async function getKv(request: Request, env: Env) {
const searchParam = new URL(request.url).searchParams.get('key');
// const allKeys = await env.KV_BINDING.list();
// console.log(allKeys);
const value = await env.KV_BINDING.get(`${searchParam}`);
if (!value) {
return new Response('Key not found', { status: 404 });
}
return new Response(value);
}
Now we will create the logic to receive the requests. The workers have methods called Handlers that allow us to receive and handle external inputs. In this case we will use fetch() for the requests and scheduled() which will be invoked by the cron trigger.
// index.ts
import { getKv, postKv } from './routes/kv';
export default {
async fetch(request, env): Promise<Response> {
if (request.method === 'POST') {
// Create a KV element
return await postKv(request, env);
}
if (request.method === 'GET') {
// Retrieve a KV element
return await getKv(request, env);
}
return new Response('Something goes wrong');
},
async scheduled(event, env, ctx): Promise<void> {
const list = await env.KV_BINDING.list({ prefix: 'task:' });
for (const key of list.keys) {
const raw = await env.KV_BINDING.get(key.name);
if (!raw) continue;
const data = JSON.parse(raw);
if (data.status === 'pending') {
console.log(`Processing: ${key.name}`);
data.status = 'processed';
const response = await fetch('https://api.resend.com/emails', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${env.RESEND_API_KEY}`,
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({
from: 'onboarding@resend.dev',
to: ['sarasa@gmail.com'],
subject: 'Hello World',
html: `<strong>I use cron triggers, ${key.name} was updated, status: ${data.status}</strong>`,
}),
});
if (!response.ok) {
console.error(`Failed to send email: ${response.status}`);
break;
}
await env.KV_BINDING.put(key.name, JSON.stringify(data));
break;
}
}
},
} satisfies ExportedHandler<Env>;
With this we make that every time that the cron Trigger is activated, it searches in the KVs for any KV that has pending status and passes it to processed and then sends us an email.
Here we can see the process:
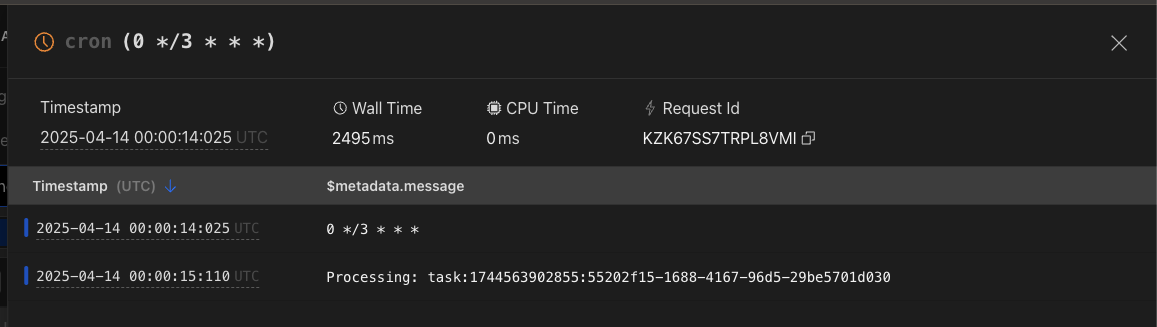

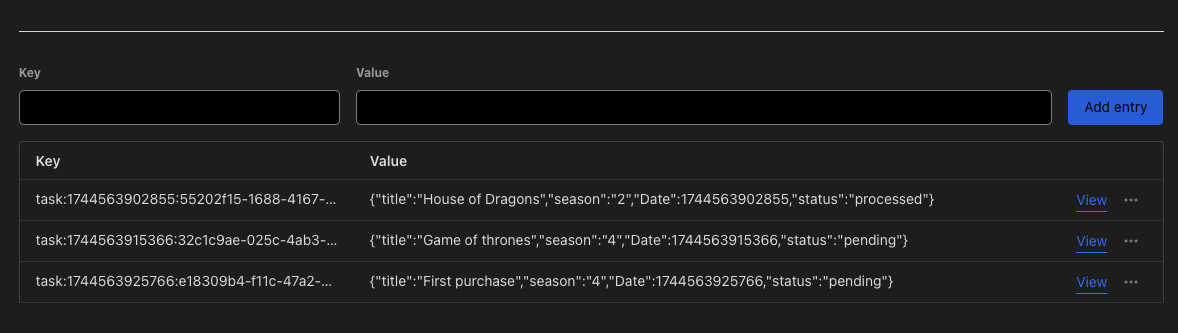
That’s it, this was a quick and easy way to create a cron trigger. You can find the code here.