Caching in Next.js
Next.js have a different ways to cache data and improve the performance in out applications.
| Mechanism | What | Where | Purpose | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Request Memoization | Return values of functions | Server | Re-use data in a React Component tree | Per-request lifecycle |
| Data Cache | Data | Server | Store data across user requests and deployments | Persistent (can be revalidated) |
| Full Route Cache | HTML and RSC payload | Server | Reduce rendering cost and improve performance | Persistent (can be revalidated) |
| Router Cache | RSC Payload | Client | Reduce server requests on navigation | User session or time-based |
By default Next.js will use cache in our application for reduce costs. By default Next.js use static render and cache data request

Request Memoization
Next.js extends the fetch API to automatically memoize requests that have the same URL and options. So if we use a same fetch call in multiple places we execute it once.
If we have a several calls to the same url with the same params we can use the request memoization for reduce the calls and HIT the cache in memory.
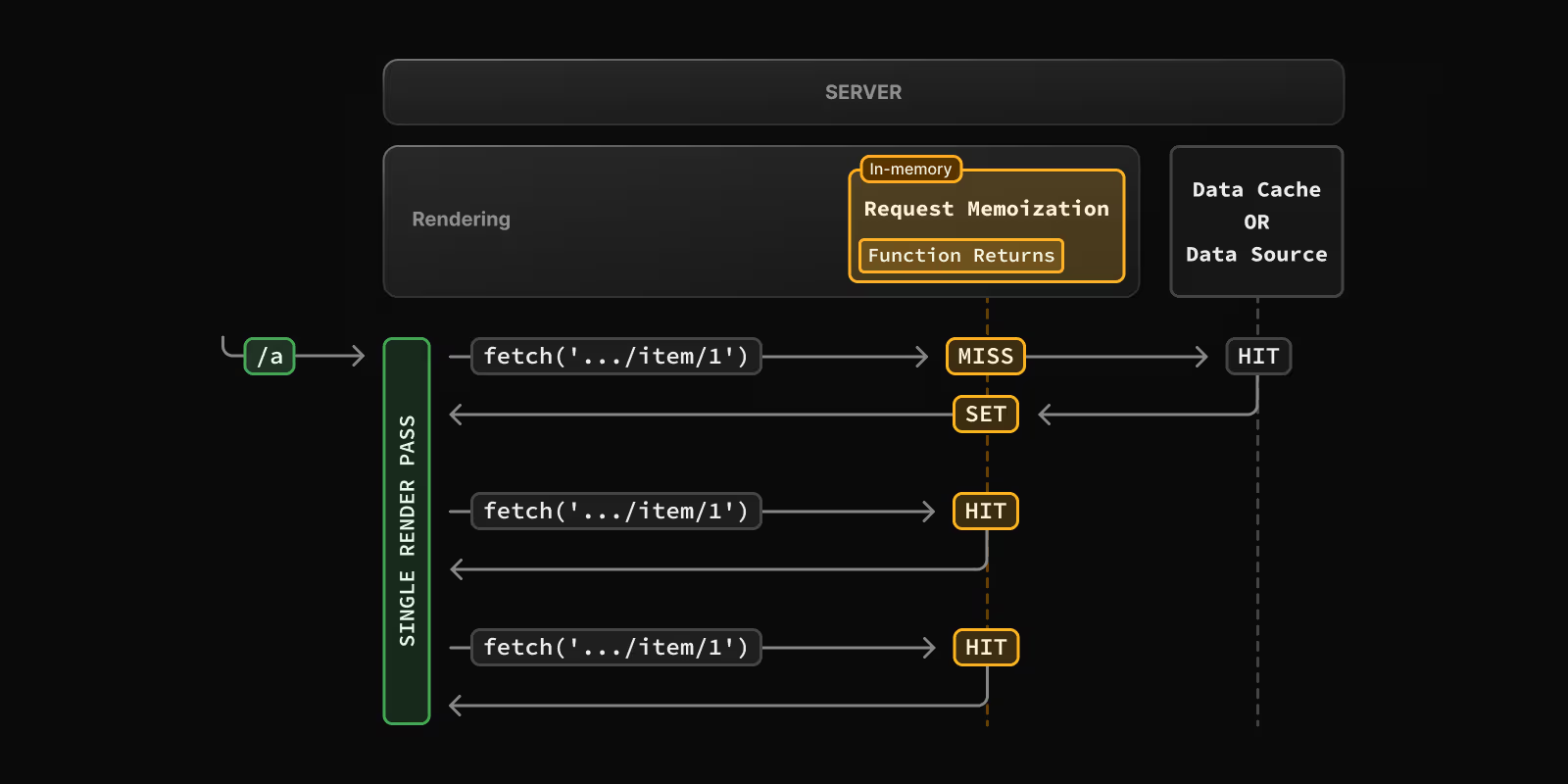
The cache lasts the lifetime of a server request until the React component tree has finished rendering.
Data Cache
Next.js has a built-in Data Cache that persists the result of data fetches across incoming server requests and deployments.
Whether the data is cached or uncached, the requests are always memoized to avoid making duplicate requests for the same data during a React render pass.
Next.js handles fetch requests like this:
- With
force-cache: checks Data Cache first; if cached, returns and memoizes. If not, fetches data, caches, and memoizes. - Without cache (
no-storeor no cache option): always fetches fresh data and memoizes. - In all cases, requests are memoized to avoid duplicates during the same render pass.
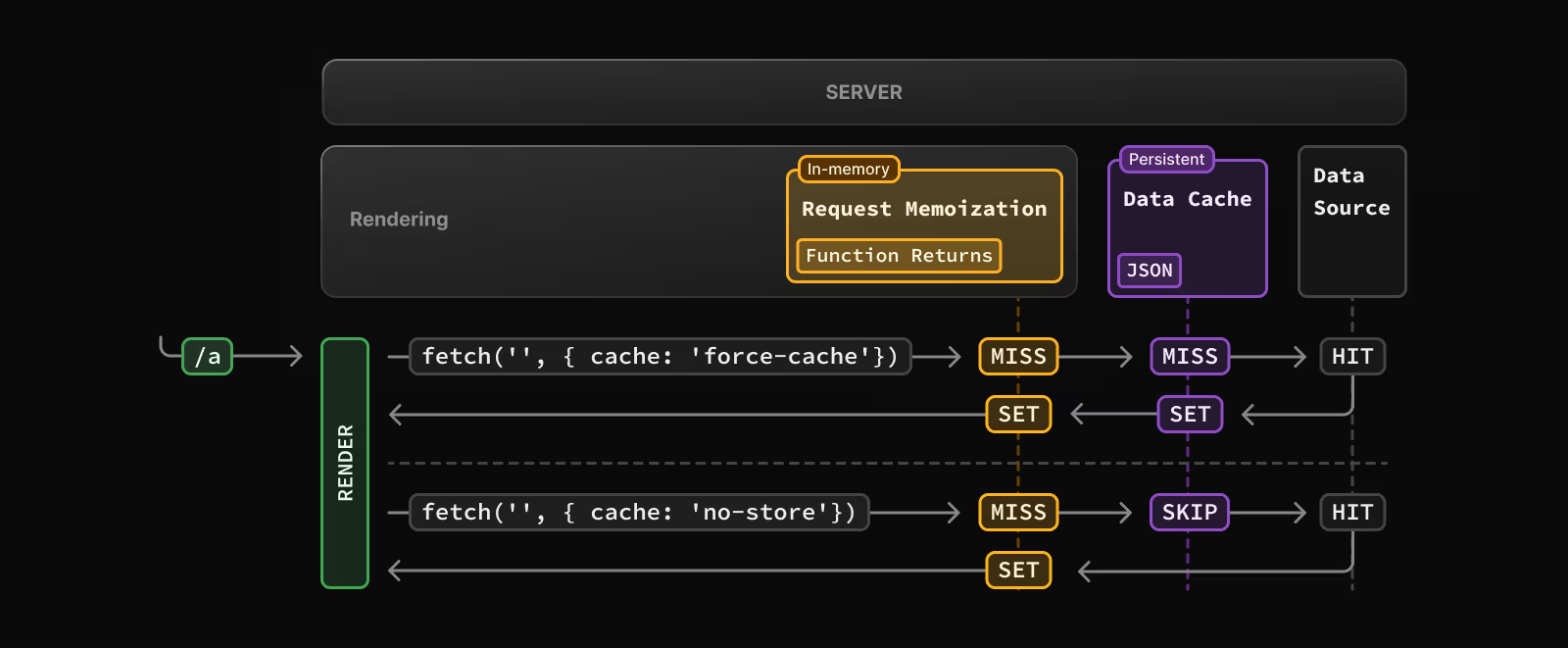 The data will persist until we revalidate again we can revalidate the data with
The data will persist until we revalidate again we can revalidate the data with On-demand Revalidation and Time-based Revalidation. See Data fetching in Next.js
Differences between the Data Cache and Request Memoization While both caching mechanisms help improve performance by re-using cached data, the Data Cache is persistent across incoming requests and deployments, whereas memoization only lasts the lifetime of a request.
Full Route Cache
The default behavior of Next.js is to cache the rendered result (React Server Component Payload and HTML) of a route on the server. This applies to statically rendered routes at build time, or during revalidation.
What is the React Server Component Payload? The React Server Component Payload is a compact binary representation of the rendered React Server Components tree. It’s used by React on the client to update the browser’s DOM.
Notes mentioning this note
There are no notes linking to this note.